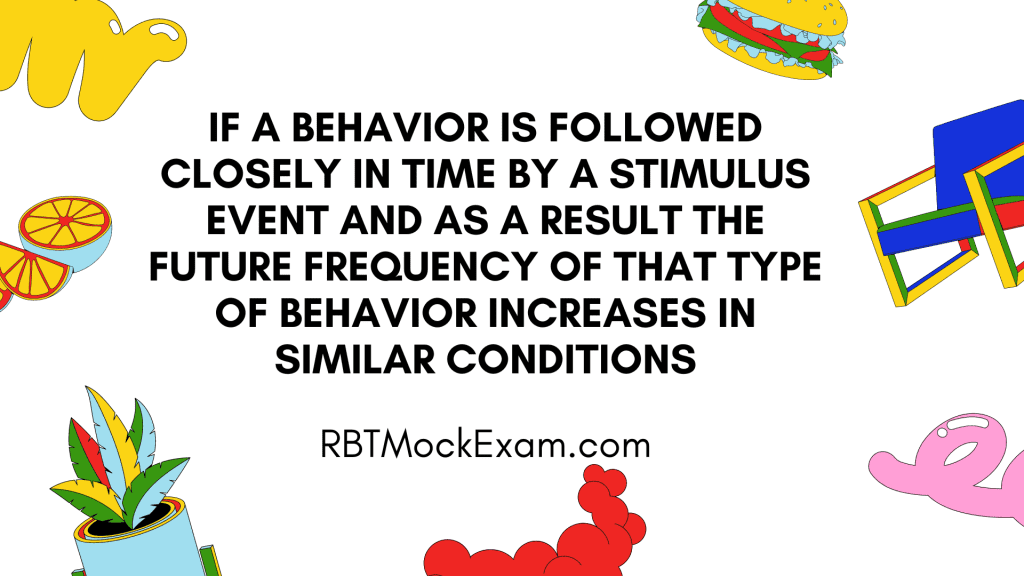
Question: “If a behavior is followed closely in time by a stimulus event and as a result the future frequency of that type of behavior increases in similar conditions” best describes which of the following?
Options:
- Punishment
- Extinction
- Reinforcement
- Conditioned Response
Correct Answer: 3. Reinforcement
Explanation: Reinforcement occurs when a behavior is followed closely in time by a stimulus event, resulting in an increase in the future frequency of that behavior under similar conditions. Reinforcement can be either positive (adding a stimulus) or negative (removing a stimulus). Still, in both cases, the effect is an increase in the behavior’s occurrence because the consequence is reinforcing.
Practice Tests On This Question
- RBT Practice Exam
- RBT Practice Test #1
- RBT Practice Exam 75 Questions
- RBT Practice Exam 85 Questions
Types of Reinforcement
- Positive Reinforcement:
- Definition: Adding a desirable stimulus following a behavior increases the likelihood of that behavior recurring.
- Example: A child receives praise (the reinforcer) after cleaning their room, making them more likely to clean again in the future.
- Key aspect: Something pleasant is added to the environment.
- Negative Reinforcement:
- Definition: The removal of an aversive stimulus following a behavior, which increases the likelihood of that behavior recurring.
- Example: A student completes their homework to avoid getting detention, making them more likely to do homework in the future.
- Key aspect: Something unpleasant is removed from the environment.
- Note: Often confused with punishment, but negative reinforcement strengthens behavior, while punishment weakens it.
- Primary Reinforcement:
- Definition: Reinforcers that satisfy basic biological needs.
- Also known as: Unconditioned reinforcers
- Examples: Food, water, sleep, physical comfort
- Key aspect: These are inherently reinforcing without need for learning.
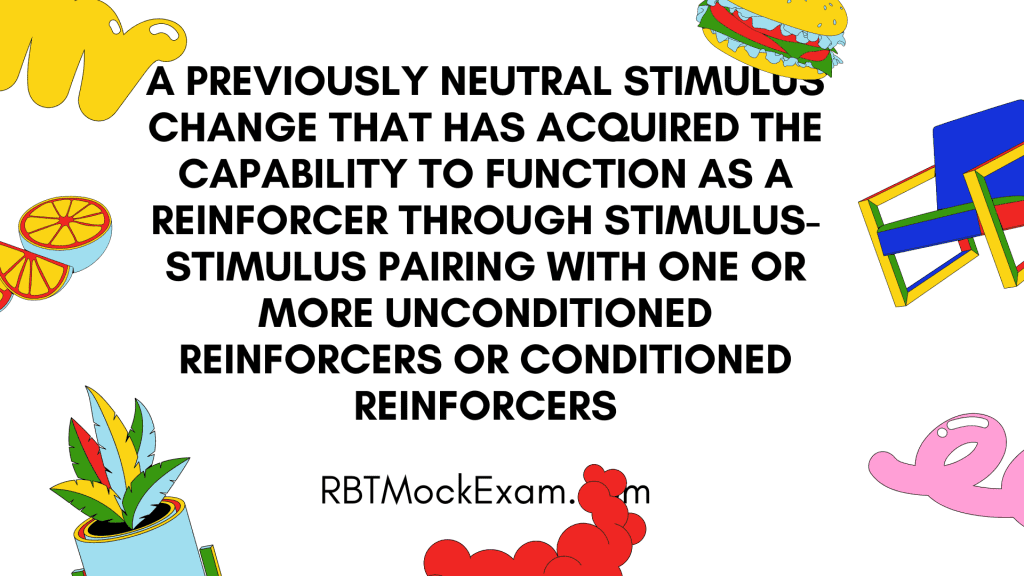
- Secondary Reinforcement:
- Definition: Reinforcers that have acquired their reinforcing properties through association with primary reinforcers or other secondary reinforcers.
- Also known as: Conditioned reinforcers
- Examples: Money, grades, social approval
- Key aspect: These become reinforcing through a learning process.
- Intrinsic Reinforcement:
- Definition: Reinforcement that comes from within the individual, often in the form of positive feelings or satisfaction.
- Example: The personal satisfaction of mastering a new skill
- Key aspect: The reinforcement is internal and not dependent on external sources.
- Extrinsic Reinforcement:
- Definition: Reinforcement that comes from external sources.
- Examples: Tangible rewards, praise from others
- Key aspect: The reinforcement is provided by the environment or other individuals.
- Social Reinforcement:
- Definition: Reinforcement that involves social interaction or approval.
- Examples: Smiles, compliments, attention
- Key aspect: Particularly important in human behavior due to our social nature.
- Token Reinforcement:
- Definition: A system where tokens are given as immediate reinforcers and can be exchanged later for other reinforcers.
- Example: A child earns stars for good behavior, which can be traded for prizes
- Key aspect: Bridges the gap between immediate and delayed reinforcement.